Trouble in Sunshine Creek
What’s going on at the Sunshine Creek Vineyard? The leaves are yellowing, plants are dying, and the invasive Glassy-Winged Sharpshooter seems to be everywhere!
Have a Meta Quest headset? Try it now.
Try the Trouble in Sunshine Creek experience in VR on any Meta Quest headset today.
Topics covered:
✓ Invasive species
✓ Plant cell biology
✓ Plant anatomy
✓ Bacterial infection
✓ Bacterial genetics
✓ Translation
-
A complex set of interactions within an ecosystem can keep its numbers and types of organisms relatively constant over long periods of time under stable conditions. If a modest biological or physical disturbance to an ecosystem occurs, it may return to its more or less original status (i.e., the ecosystem is resilient), as opposed to becoming a very different ecosystem. Extreme fluctuations in conditions or the size of any population, however, can challenge the functioning of ecosystems in terms of resources and habitat availability.
Moreover, anthropogenic changes (induced by human activity) in the environment—including habitat destruction, pollution, introduction of invasive species, overexploitation, and climate change—can disrupt an ecosystem and threaten the survival of some species.
-
Humans depend on the living world for the resources and other benefits provided by biodiversity. But human activity is also having adverse impacts on biodiversity through overpopulation, overexploitation, habitat destruction, pollution, introduction of invasive species, and climate change. Thus sustaining biodiversity so that ecosystem functioning and productivity are maintained is essential to supporting and enhancing life on Earth. Sustaining biodiversity also aids humanity by preserving landscapes of recreational or inspirational value.
NGSS Standards
Based on research from
by Elizabeth G. Clark, Ph.D
12 Interactive Environments
Our 3D worlds comprise of multiple linked environments for students to zoom into and explore, connecting the macro with micro contexts for understanding.
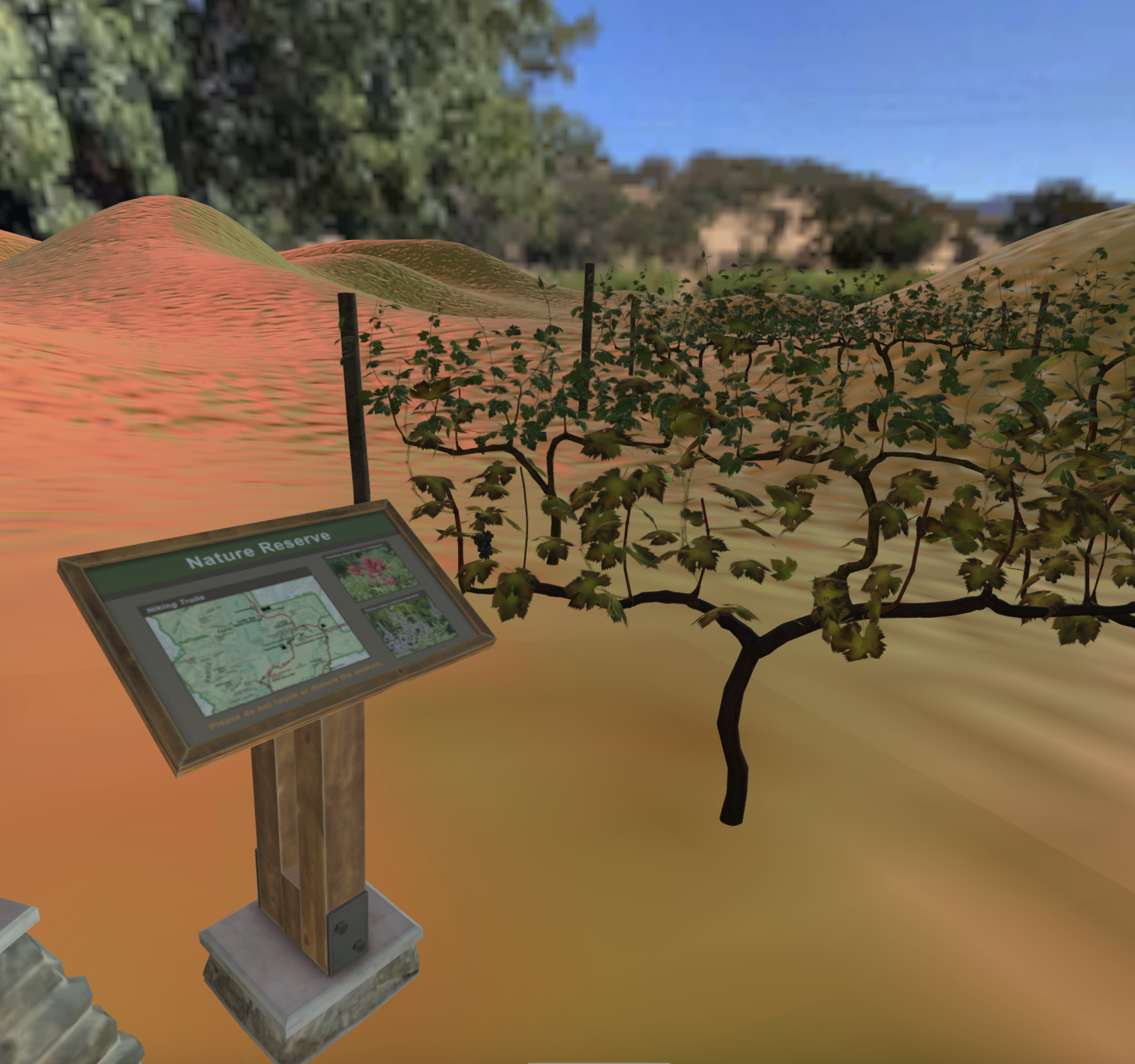
Sunshine Creek Vineyard
Welcome to the Sunshine Creek vineyard, half of which looks wilted. Explore the difference between the healthy and unhealthy half of the vineyard by zooming into each plant.
Healthy Grapevine
Zoom into the the surface of the grapevine stem, where you can see what vibrant leaves and giant grapes of a healthy plant look like.
Unhealthy Grapevine
Take a look at the unhealthy half of the vineyard and see the difference in scorched leaves, and the presence of invasive bugs on this plant!
Healthy Stem
A healthy leaf stem cross-section shows the xylem, phloem, and 3D structure within the stem.
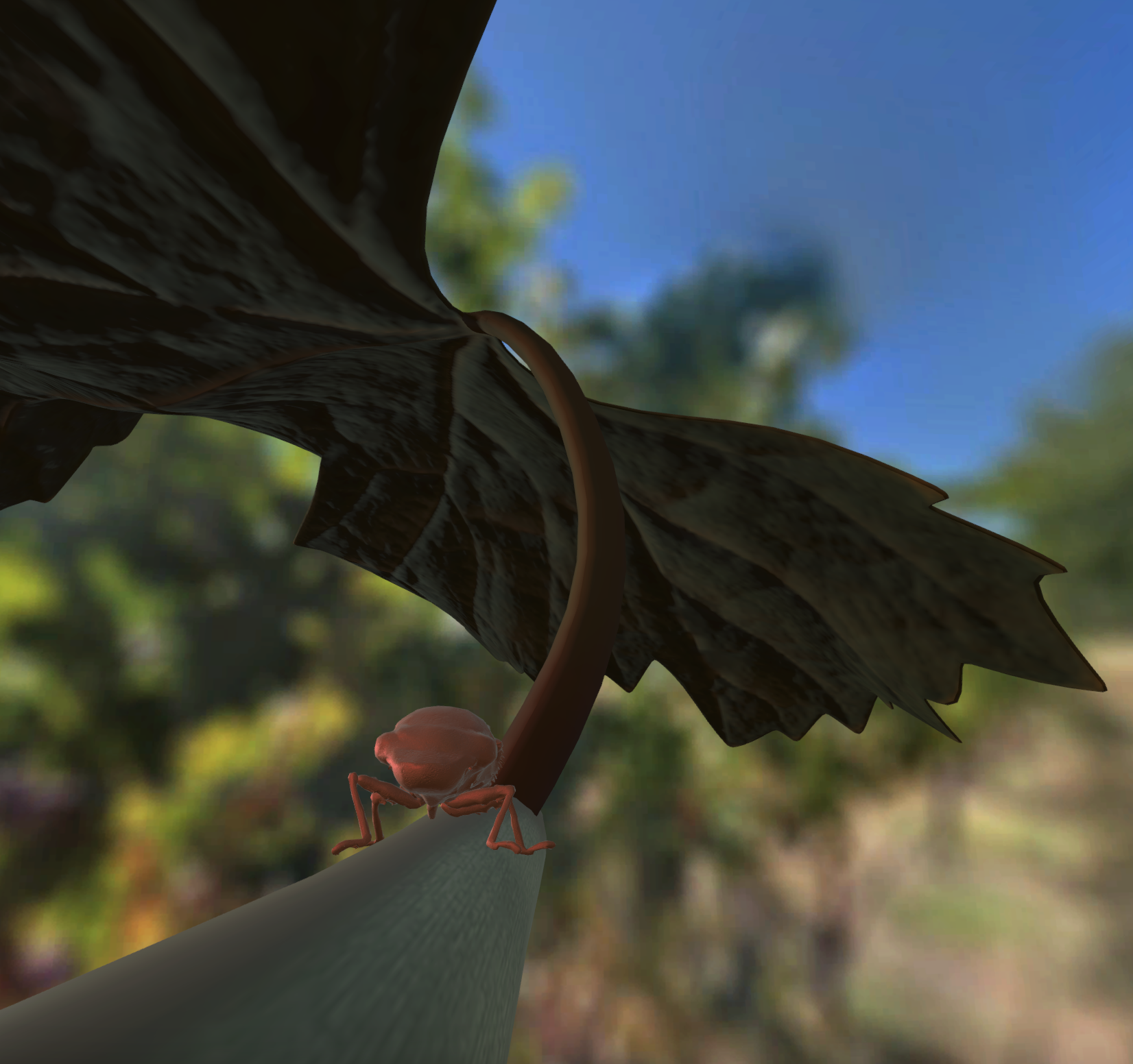
Unhealthy Stem
The unhealthy leaf stem reveals the Glassy Winged Sharpshooter insect proboscis inserted into the stem, and bacteria present on the xylem!
Healthy Leaf
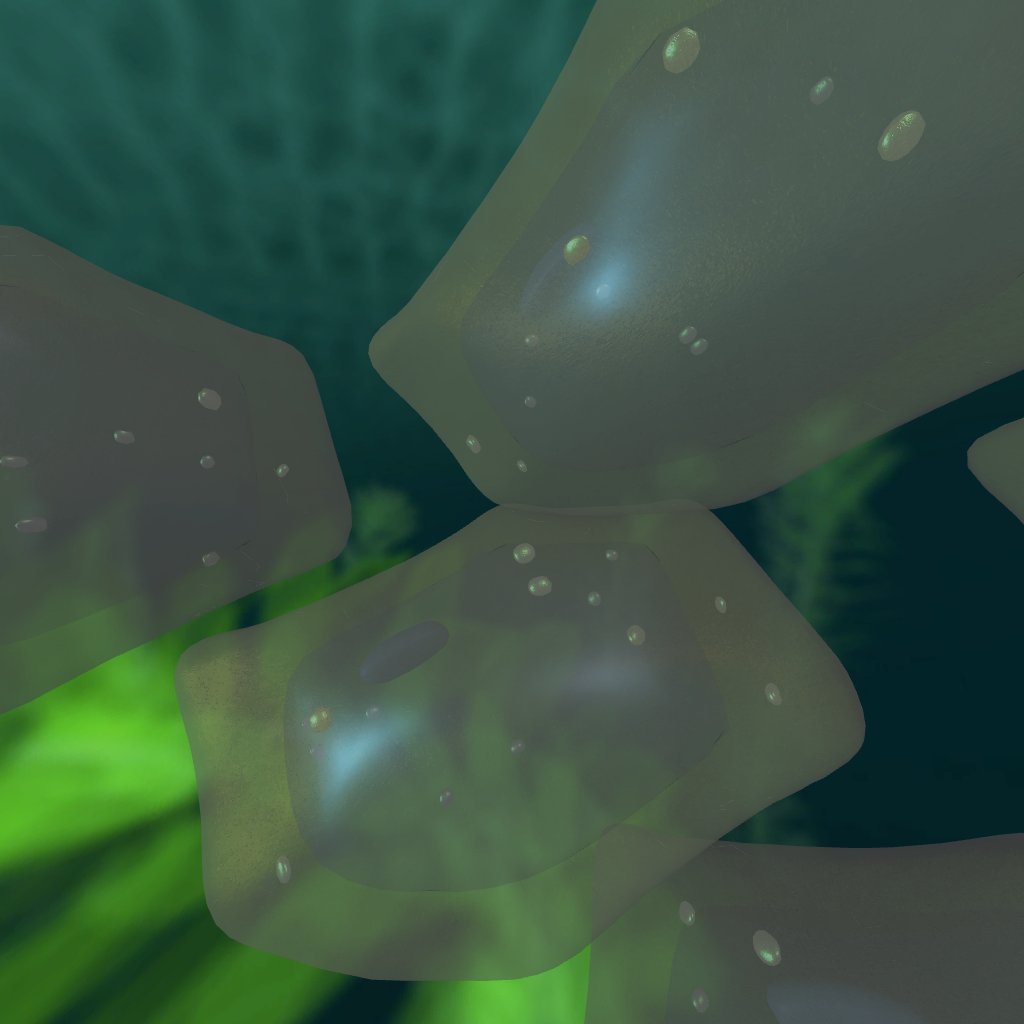
Zoom into a healthy grapevine leaf to see what green and plump healthy, hydrated leaf cells look like.
Unhealthy Leaf
In contrast, zoom into an infected leaf cell to see the difference between hydrated leaf cells and dull, dehydrated leaf cells.
Leaf Cell
Inside the leaf cell, you can find a multitude of organelles, including the chloroplast, mitochondria, golgi apparatus, kinesin, microtubules, ER, and the nucleus.
Xylem Vessel Healthy
Enter the xylem vessel of a healthy stem to see free-flowing sap and learn about how plants transport energy through the xylem vessel.
Xylem Vessel Unhealthy
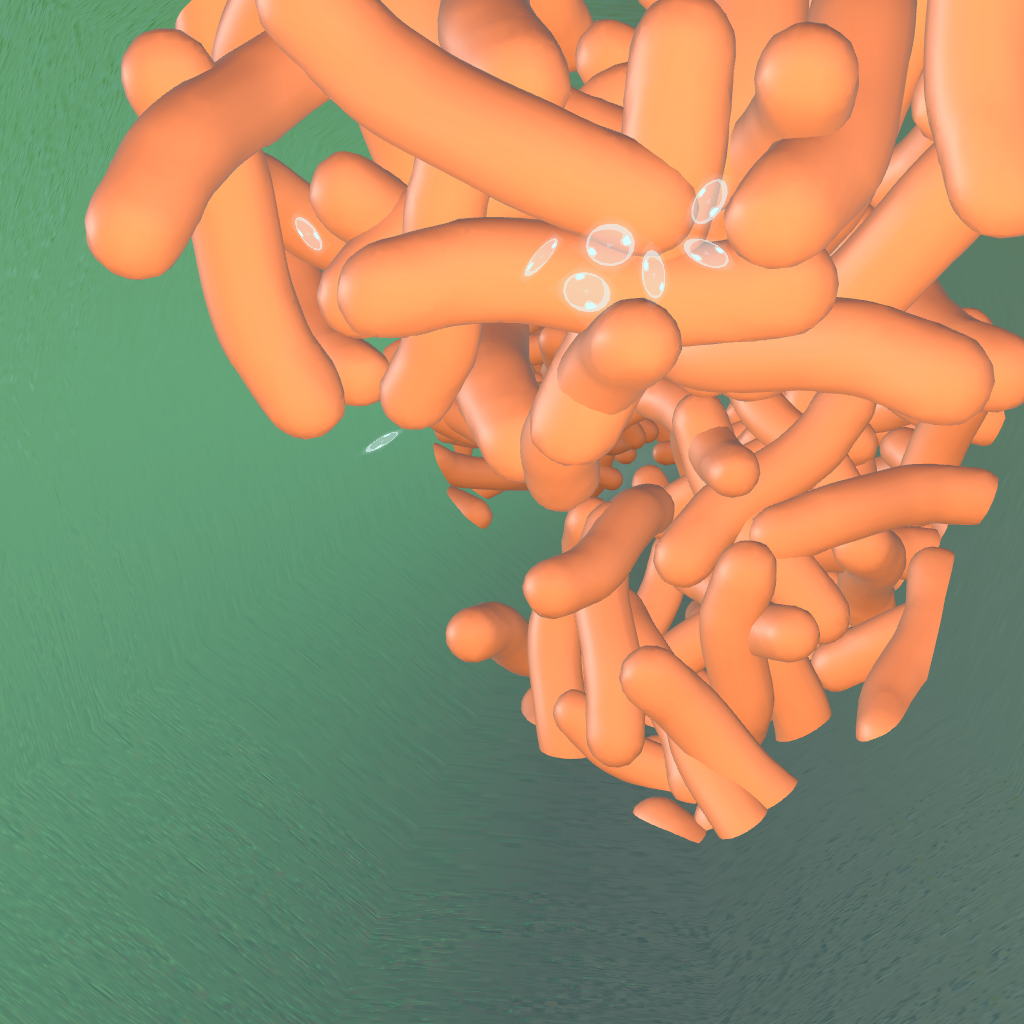
Inside the unhealthy xylem vessel, you can see the presence of several bacteria blocking the path of the sap traveling through the vessel.
Xylella Fastidiosa
Zoom into the bacteria cell to see within the lipid layer, with ribosome moving along mRNA, surrounded by DNA, tRNA, and peptide chains.
Treat with antibiotic
Treat this bacteria with antibiotics and see the molecular result of stopping the ribosome from moving. Zoom out into the rest of the vineyard to see the effect of the treatment!
AI Voice Guide
Students are guided through every experience by our AI Guide which audibly informs, instructs and prompts them with questions throughout.
Real-time Feedback & Reporting
Students answer the prompts verbally. AI gives them real-time feedback, and surfaces their understanding in the Educator Dashboard.
Immersive & Interactive
Every object is interactive in each environment. As students explore, they can select elements to learn about them in context.
Real in-app student responses:
See all of our immersive science experiences.
Experience 10k Science for yourself
Try our VR viewer on the Meta Quest, or contact us to set up a demo and inquire about getting 10k Science for your class!